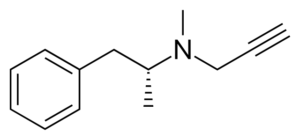
Selegiline is an MAO enzyme inhibitor that preferentially inhibits MAO-B at the doses commonly used. In medical settings, it is used for Parkinson’s disease and depression. It’s been investigated for other conditions.
The drug is largely void of recreational effects, but it can anecdotally increase motivation and provide some mood improvement. Selegiline is sometimes taken for its potential nootropic and life extension properties.
At common doses, the substance functions by altering dopamine and phenethylamine activity.
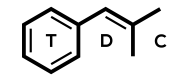
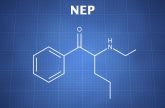
Selegiline = Deprenyl; L-deprenyl; (R)-9CI; (-)-Deprenyl; R-Deprenyl; E-250; N,a-Dimethyl-N-2-propynyl; (R)-N-methyl-N-(1-phenylpropan-2-yl)prop-1-yn-3-amine
Dose
Oral (medical)
Parkinson’s: 10 mg
Depression: 30 – 60 mg/day
Oral/Buccal (medical)
Parkinson’s: 1.25 mg
Transdermal (medical)
Total: 6 – 12 mg/day
Oral
Common: 5 – 10 mg
Full range: 1 mg – 10 mg
Timeline
Oral
Subjective: Possibly greatest during the first few hours
Total: Inexact, 24+ hours for MAO inhibition (once daily dosing is used)
Experience Reports
References
(2014) Comparative efficacy of selegiline versus rasagiline in the treatment of early Parkinson’s disease.
(2012) A critical review of evidence for preclinical differences between rasagiline and selegiline
(2012) Selegiline: a reappraisal of its role in Parkinson disease.
(2012) Selegiline transdermal system (STS) as an aid for smoking cessation.
(2011) The pharmacology of selegiline.
(2010) R-deprenyl: pharmacological spectrum of its activity.
(2004) Transdermal selegiline and intravenous cocaine: safety and interactions.
(2003) Selegiline for Alzheimer’s disease.
(2002) Neuroprotective actions of selegiline.
(2000) (-)Deprenyl (Selegiline): past, present and future.
(1997) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of selegiline. An update.
(1996) Selegiline is neuroprotective in primary brain cultures treated with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium.
(1996) Pharmacology of selegiline.
(1994) Therapy with l-deprenyl (selegiline) and relation to abuse liability.
(1994) Amphetamine-like effect of l-deprenyl (selegiline) in drug discrimination studies.
(1992) The molecular pharmacology of L-deprenyl
(1991) A review of the pharmacology of selegiline.
(1987) Cognitive effects of L-deprenyl in Alzheimer’s disease.
(1983) Deprenyl (selegiline): the history of its development and pharmacological action.