Gabapentin is a GABA-like drug that has been used medically in the treatment of epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and other conditions.
It has also been used recreationally due to its anxiolytic, sedative, and euphoriant effects.
Even at high strong+ doses, gabapentin is relatively safe physically, but there are still risks and it can certainly cause death.
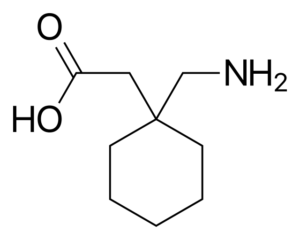
Gabapentin = Neurontin; 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid
Dose
Oral
Light: 300 – 600 mg
Common: 600 – 900 mg
Strong: 900 – 1200+ mg
Timeline
Oral
Total: 5 – 8 hours
Onset: 00:30 – 01:30
Experience Reports
References
(2014) Profiles of pregabalin and gabapentin abuse by postmortem toxicology.
(2014) Misuse and abuse of pregabalin and gabapentin: cause for concern?
(2014) Gabapentin for Substance Use Disorders: Is it Safe and Appropriate?
(2014) Potential misuse of pregabalin and gabapentin
(2013) Implications and mechanism of action of gabapentin in neuropathic pain.
(2012) Substance misuse of gabapentin
(2011) Suicide by gabapentin overdose.
(2010) A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin.
(2010) Anticonvulsant medications and the risk of suicide, attempted suicide, or violent death.
(2009) Gabapentin toxicity in renal failure: the importance of dose adjustment.
(2006) The mechanisms of action of gabapentin and pregabalin.
(2005) Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain.
(2002) Gabapentin: pharmacology and its use in pain management.
(2002) Inhibition of neuronal Ca(2+) influx by gabapentin and pregabalin in the human neocortex.
(2001) Gabapentin-induced hypersensitivity syndrome.
(1998) A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology.
(1998) Gabapentin as a potential treatment for anxiety disorders.
(1997) Gabapentin in the treatment of bipolar disorder
(1996) The effect of gabapentin on brain gamma-aminobutyric acid in patients with epilepsy.
(1994) Lack of serious toxicity following gabapentin overdose.