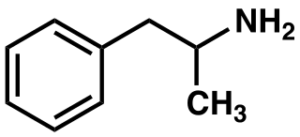
Adderall is a combination of dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine that is commonly prescribed for ADHD. It effectively combats ADHD in many people, and in healthy users, it can provide an acute cognitive boost. Because of its cognition enhancing and stimulant properties, adderall is commonly used by students and workers.
In normal medical settings with a common medical dose, adderall doesn’t appear to be notably harmful and it appears useful (at least on a time scale of 1-2 years) in those with ADHD.
The drug can provide wakefulness and improve attentiveness, motivation, cognitive performance, and physical performance. Outside of medical settings, tolerance will usually kick in quickly and remove many of the beneficial effects.
Adderall = Amphetamine; Adderall XR
Dose
Oral
Light: 5 – 15 mg
Common: 15 – 40 mg
Strong: 40 – 75 mg
Intranasal
Light: 5 – 10 mg
Common: 10 – 30 mg
Strong: 30 – 50 mg
Timeline
Oral
Total: 3 – 5 hours (extended to 6 – 10 hours with Adderall XR)
Onset: 00:10 – 00:30 (extended to 00:20 – 01:00 with Adderall XR)
Intranasal
Total: 2 – 4 hours
Onset: 00:01 – 00:05
Experience Reports
References
(2016) Amphetamines for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents
(2014) Psychostimulants and Cognition: A Continuum of Behavioral and Cognitive Activation
(2013) Amphetamine, past and present – a pharmacological and clinical perspective
(2011) Amphetamines for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in adults
(2011) ADHD Drugs and Serious Cardiovascular Events in Children and Young Adults
(2009) Potential adverse effects of amphetamine treatment on brain and behavior: a review
(1974) Long-term administration of d-amphetamine: Progressive augmentation of motor activity and stereotypy
(1957) Amphetamine Psychosis
Test Results